
Expanded Carrier Screening (ECS)
Expanded Carrier Screening (ECS)
Carrier screening is a type of genetic test to identify whether you and/or your partner are carriers of a genetic disorder which can be passed on to your next generation. A single blood sample can test for over 300 genetic disorders. ECS can provide additional genetic information to the couple and assess the risk of passing on single-gene disorders to the next generation.
What is a carrier?
A carrier is a person who silently carries an affected or mutated gene without presenting any symptoms or with mild symptoms. If you and your partner are both carriers of the same disorder, there is a 25% chance that your baby will be affected by the same disorder except for X-linked recessive disorders.
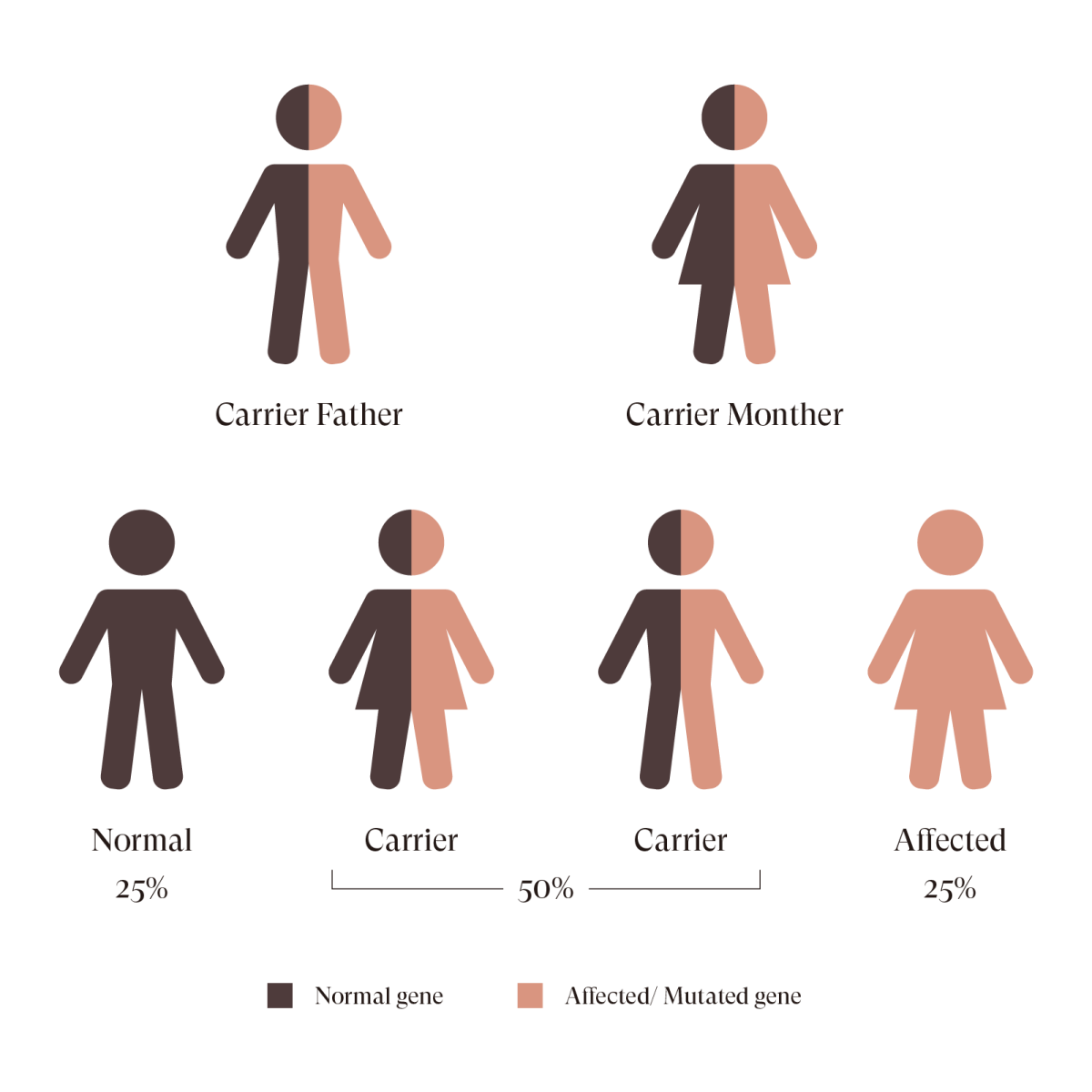
Carriers are generally not aware of their carrier status as they are usually not presenting with any symptoms or just present with mild symptoms.
Who should consider ECS?
- Couples planning for a pregnancy or in early pregnancy who have never done any genetic carrier screening;
- Couples who consider conceiving through assisted reproductive technology
- Egg and sperm donors for reproductively challenged couples
- Patients with a history of recurrent miscarriages;
- Patients with a history of abnormal pregnancy;
- Couples who are biologically related;
- Patients with family history of genetic disorders
Which genetic diseases can be picked up by the screening?
The American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) and The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommend all women who are considering pregnancy or are already pregnant should conduct carrier screening for specific genetic disorders such as spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), cystic fibrosis (CF), thalassemia and haemoglobinopathies and fragile X premutation etc. Additional screening may also be indicated based on family history or specific ethnicity. Please consult your doctor for more details.
Screening Procedure
- Pre-test Genetic Counselling
- Blood sampling
- Send to the lab for Expanded Carrier Screening
- Report (around 3-4 weeks)
Service Leaflet
FAQ
Q: When should I undergo Expanded Carrier Screening (ECS)?
A: ECS screening is recommended to be done before pregnancy or in early pregnancy, allowing couples to make informed decisions in family planning.
Q: If my test results are negative, does it mean my baby is free from all genetic disorders?
A: ECS can only detect certain genetic mutations associated with known hereditary diseases. It cannot detect all genetic disorders, nor does it apply to all known hereditary diseases.
This test cannot completely rule out the possibility of your baby being affected by genetic disorders, it can only reduce the risk of passing on certain genetic disorders to the embryos. Therefore, it cannot guarantee that your baby will be completely healthy.
Q: What are the choices if my partner and I are carriers of a genetic disorder?
A:
- Conceive naturally and perform a prenatal diagnostic test to see if the fetus has the disorder.
- You can choose to use assisted reproductive technologies (e.g. IVF and PGT) to reduce the risk of having a baby with the disorder.
- You may choose not to get pregnant or consider adoption.



